Handling events
To handle incoming events, the only thing you need is a or multiple REST endpoints on your backend. KNOT SVaaS will make a HTTP POST on the endpoints you configured on the manager.
The system is flexible, you can create a route by events or group several events on the same route. Organize yourself as you want!
Configure endpoints
To configure endpoints, please go on our manager:
Then open the menu API Keys and click on Add endpoints:
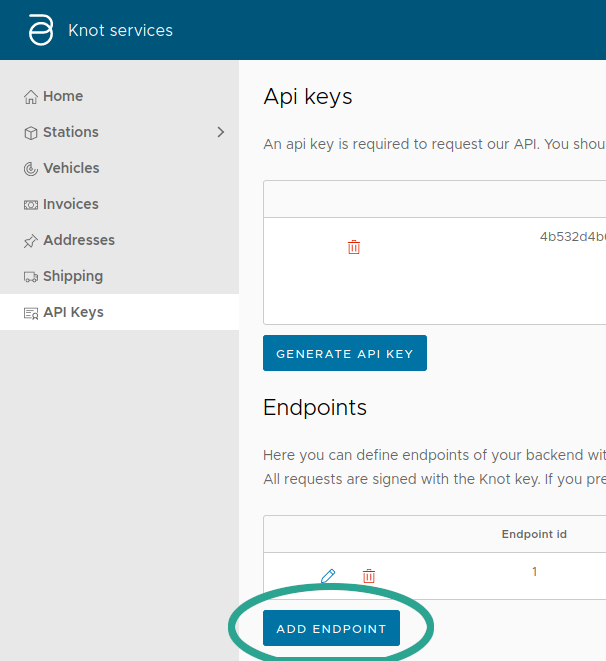
Then you need to complete the form.
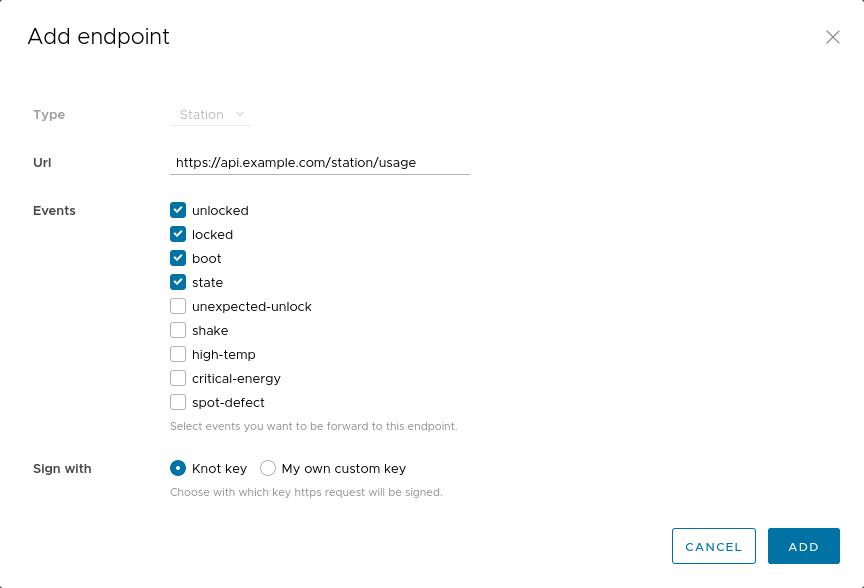
- Type:
stationorvehicle. - Url: Here you should put the url of your endpoint.
- Events: Choose one or more events to be sent to this endpoint. In this example we check all event related to a normal usage of the station. The 5 others are related to alert / problem handling.
- By default the request is signed with the KNOT private key, but you can specify your own key if you prefer.
Verify request signature
To ensure that the request come from KNOT and not from an attacker, you should verify the signature of the request.
Example of implementation
Here is a simple implementation in NodeJS with express
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const rent = require('./core/rent-system');
app.post('/station/usages', (req, res) => {
const station = req.body.station;
const event = req.body.event;
if (event == "boot") {
console.log(`Station #${station} booted !`);
}
else if (event == "unlocked") {
const spot = req.body.data.spot;
const unlockId = req.body.data.unlock;
console.log(`Spot ${spot} on station #${station} has been unlock`);
rent.start(unlockId);
}
else if (event == "locked") {
const spot = req.body.data.spot;
const scooterId = req.body.data.vehicle;
const date = new Date(req.body.data.time);
console.log(`Scooter #${scooterId} returned spot ${spot} on station #${station} at ${date.toISOString()}`);
rent.stop(scooterId, date);
}
res.status(200).end();
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Example app listening on port 3000!');
});